Quick Summary: Master Amazon S3 bucket creation with this comprehensive guide covering setup, security, cost optimization, and best practices. Perfect for developers, system administrators, and cloud architects looking to leverage AWS storage effectively.
Amazon S3 bucket creation is a fundamental skill every cloud developer must master. With Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) powering millions of applications worldwide, understanding how to create and configure S3 buckets properly can make the difference between a secure, cost-effective storage solution and a potential security nightmare.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic Amazon S3 setup to advanced configuration strategies, helping you build scalable and secure cloud storage infrastructure.
Why Amazon S3 Matters for Your Business
📈 Unlimited Scalability
Scale from gigabytes to petabytes instantly without infrastructure changes or capacity planning.
🔒 Enterprise Security
Built-in encryption and access controls protect your data with industry-leading security standards.
💰 Cost Optimized
Pay only for what you use with intelligent storage class transitions and lifecycle management.
🌍 Global Availability
99.999999999% (11 9’s) durability with worldwide regional availability for optimal performance.
Prerequisites: Setting Up Your AWS Environment
Before creating your first S3 bucket, ensure you have the proper AWS foundation in place:
Step-by-Step: Creating Your First S3 Bucket
Method 1: Using the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console provides the most user-friendly approach to S3 bucket creation:
- Access the S3 Console: Navigate to
console.aws.amazon.com/s3/or search for “S3” in the AWS services menu. - Initiate Bucket Creation: Click the orange “Create bucket” button to open the configuration dialog.
- Configure Basic Settings: Enter your bucket name and select the appropriate AWS region for your use case.
- Set Security Options: Configure Block Public Access settings, versioning, and default encryption.
- Review and Create: Verify your settings and click “Create bucket” to finalize the process.
Method 2: Using AWS CLI
For automation and scripting, the AWS CLI provides powerful bucket creation capabilities:
Basic CLI Command
aws s3 mb s3://your-unique-bucket-name --region us-east-1
This creates a basic S3 bucket with default settings in the specified region.
S3 Bucket Naming: Getting It Right
Proper S3 bucket naming is critical because bucket names must be globally unique across all AWS accounts worldwide. Here’s what you need to know:
S3 Naming Rules (Non-negotiable)
- Bucket names must be 3-63 characters long
- Use only lowercase letters, numbers, dots (.), and hyphens (-)
- Must start and end with a letter or number
- Cannot contain spaces or uppercase letters
- Must not be formatted as an IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1)
- Cannot contain consecutive dots or end with specific suffixes
Strategic Naming Examples
💡 Pro Tip: Naming Strategy
Develop a consistent naming convention that includes your organization name, environment (prod/dev/test), purpose, and region. This approach minimizes naming conflicts and improves bucket management at scale.
Security First: Modern S3 Protection
AWS has significantly enhanced S3 security defaults, but understanding these features is essential for proper configuration.
Block Public Access: Your First Line of Defense
AWS automatically enables Block Public Access for new S3 buckets, providing four layers of protection:
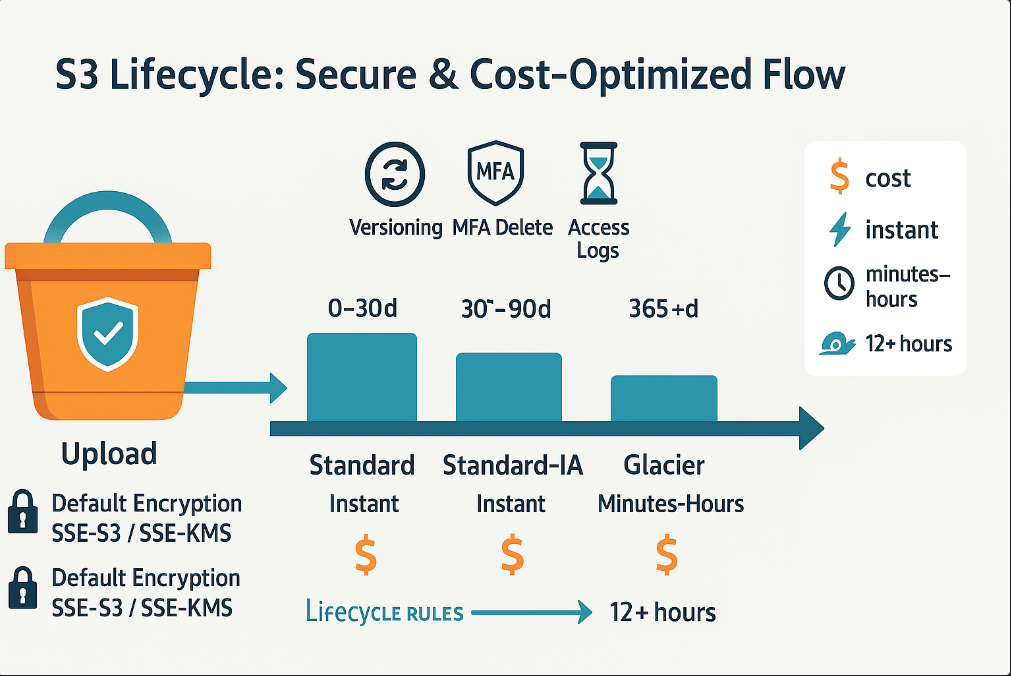
Lifecycle Policy Examples
Implement these common lifecycle patterns to automate cost optimization:
- Log Management: Move application logs to Infrequent Access after 30 days, then to Glacier after 90 days
- Backup Optimization: Transition backups to Deep Archive for long-term retention
- Development Cleanup: Automatically delete temporary files and incomplete uploads
- Media Archives: Use Intelligent-Tiering for unpredictable access patterns
Advanced Configuration Options
Versioning and Object Protection
Enable S3 versioning to protect against accidental deletions and modifications. This feature:
- Maintains multiple versions of each object
- Allows recovery from unintended changes
- Supports compliance requirements for data retention
- Works seamlessly with lifecycle policies
Cross-Region Replication
Set up Cross-Region Replication (CRR) for:
- Disaster Recovery: Maintain copies in different geographic regions
- Compliance: Meet data residency requirements
- Performance: Serve content from regions closer to users
- Security: Maintain backup copies for critical data
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Avoid these frequent S3 mistakes that can impact security, performance, and costs:
Monitoring and Maintenance
CloudWatch Metrics
Set up monitoring for these key S3 metrics:
- Storage Utilization: Track bucket size growth over time
- Request Metrics: Monitor GET, PUT, and DELETE operations
- Error Rates: Identify and respond to 4xx and 5xx errors
- Data Transfer: Track bandwidth usage and associated costs
Cost Management
Implement ongoing cost optimization with:
- S3 Storage Lens: Comprehensive storage analytics and optimization recommendations
- Cost Allocation Tags: Track costs by department, project, or environment
- Regular Access Reviews: Identify unused data for archival or deletion
- Reserved Capacity: Purchase reserved capacity for predictable workloads
Integration Patterns and Use Cases
🌐 Static Website Hosting
Host static websites directly from S3, eliminating traditional web servers. Combine with CloudFront for global content delivery.
🏗️ Data Lake Architecture
Store structured and unstructured data in various formats. Process with services like Athena, Glue, and EMR.
📱 Application Storage
Store user uploads, application assets, and dynamic content with high availability and durability.
🔄 Backup & Recovery
Reliable backup destination with cross-region replication and versioning capabilities for disaster recovery.
Troubleshooting Guide
Access Denied Errors
When encountering S3 access denied errors, check these items systematically:
- IAM Permissions: Verify the user or role has necessary S3 actions in their policy
- Bucket Policies: Look for explicit deny statements that might block access
- Block Public Access: Check if these settings are preventing legitimate access
- Resource ARNs: Ensure bucket and object ARNs are correctly specified in policies
Performance Issues
Optimize S3 performance with these strategies:
- Request Patterns: Distribute requests across different prefixes to avoid hot spots
- Multipart Uploads: Use for large files to improve upload reliability and speed
- Transfer Acceleration: Enable for faster uploads from distant locations
- CloudFront Integration: Cache frequently accessed content at edge locations
Frequently Asked Questions: Amazon S3 & S3 Bucket Creation
How much does Amazon S3 cost for S3 bucket creation and storage?
Amazon S3 pricing varies by region and storage class. During S3 bucket creation, choices like region, default encryption, versioning, and storage class (S3 Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Standard-IA, Glacier) influence cost. You pay for storage used, requests, and data transfer. The AWS Free Tier includes 5GB of Amazon S3 Standard storage, 20,000 GET, and 2,000 PUT requests per month for the first year.
Can I change my Amazon S3 bucket name after S3 bucket creation?
No. After S3 bucket creation, bucket names cannot be changed in Amazon S3. To use a different name, create a new bucket and migrate your data. Plan your Amazon S3 naming strategy in advance (organization, environment, purpose, region) to avoid costly renames.
How many objects can I store in an Amazon S3 bucket?
Amazon S3 has no limit on the number of objects per bucket. You can store unlimited objects, and each object can be up to 5 TB in size. During S3 bucket creation, focus on naming, region, and lifecycle rules rather than capacity constraints.
Is my data automatically backed up in Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 provides 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability by storing data redundantly across multiple devices and facilities. This protects against hardware failures but not accidental deletion or overwrite. As part of S3 bucket creation or right after, enable versioning, consider Object Lock (WORM), and use Cross-Region Replication (CRR) for disaster recovery.
Can I access Amazon S3 from outside AWS?
Yes. Amazon S3 exposes REST APIs, SDKs, and the AWS CLI for secure access from anywhere on the internet. After S3 bucket creation, control external access with IAM policies, bucket policies, and pre-signed URLs.
Which AWS Region should I choose during S3 bucket creation?
Pick the Amazon S3 region closest to your users or compute for lower latency and consider compliance/data-residency requirements. Region choice made at S3 bucket creation time cannot be changed later; you’d need to replicate or migrate data to another region if requirements change.
How do I enable default encryption in Amazon S3?
During or after S3 bucket creation, enable Default Encryption at the bucket level. Choose SSE-S3 (Amazon S3 managed keys) or SSE-KMS (AWS KMS managed keys or customer-managed keys). This ensures all new objects are encrypted at rest automatically.
What’s the difference between an Amazon S3 bucket policy and an IAM policy?
An IAM policy is identity-based (attached to users, roles, or groups) and grants Amazon S3 permissions to that identity. A bucket policy is resource-based (attached to the bucket) and defines who can access the bucket and objects. Most deployments use both for precise control after S3 bucket creation.
How do I host a static website on Amazon S3 securely?
Enable static website hosting on the bucket (or serve privately through Amazon CloudFront). Best practice is to keep Block Public Access enabled and use CloudFront with an Origin Access Control (OAC)</strong) to restrict direct S3 access. Configure this right after S3 bucket creation to avoid public exposure.
Does Amazon S3 provide strong read-after-write consistency?
Yes. Amazon S3 offers strong read-after-write consistency for PUTs of new objects and for overwrite/DELETE operations in all Regions. This simplifies application design after S3 bucket creation—new writes are immediately visible for subsequent reads.
How do I set lifecycle rules in Amazon S3 to control costs?
After S3 bucket creation, add Lifecycle rules to transition objects between storage classes (e.g., Standard → Standard-IA → Glacier) and to expire old versions or delete data after a set period. In the console, open your bucket → Management tab → Lifecycle rules.
What are Amazon S3 Access Points and when should I use them?
Amazon S3 Access Points provide dedicated, named network endpoints with their own policies for shared datasets. They simplify permissions when many applications or teams access the same bucket. Consider adding access points soon after S3 bucket creation for multi-tenant analytics or data-lake scenarios.
Next Steps and Advanced Topics
Once you’ve mastered basic S3 bucket creation, consider exploring these advanced topics:
- S3 Batch Operations: Perform large-scale operations across millions of objects
- S3 Object Lock: Implement WORM (Write Once, Read Many) capabilities for compliance
- S3 Access Points: Simplify access management for shared datasets
- S3 Multi-Region Access Points: Provide global endpoints for multi-region applications
Conclusion
Creating Amazon S3 buckets is more than just clicking a button—it’s about building a foundation for scalable, secure, and cost-effective cloud storage. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll avoid common pitfalls and create S3 infrastructure that grows with your needs.
Remember that S3 bucket creation is just the beginning. Ongoing optimization, monitoring, and security management ensure your AWS storage infrastructure continues to meet evolving business requirements. Start with proper planning, implement strong security controls from day one, and continuously optimize for cost and performance.
🎯 Key Takeaways
- Plan your bucket naming strategy before creation
- Implement security controls and monitoring from the start
- Use lifecycle policies to optimize costs automatically
- Monitor usage and performance regularly
- Stay informed about new S3 features and best practices
The bottom line: AWS S3 remains one of the most versatile and cost-effective cloud storage solutions available today. However, maximizing its value requires understanding all pricing nuances and implementing targeted optimization techniques. With the knowledge and strategies presented in this guide, you’re now equipped to make informed decisions that balance performance requirements with budget constraints for your organization’s cloud storage needs.
Ready to master S3 bucket creation?
Ready to master S3 bucket creation? Begin with the AWS Management Console and remember: successful S3 deployment starts with proper planning and continues with ongoing optimization. Happy S3 bucket creating!
Join 500+ companies already saving with intelligent cloud cost optimization.