As with any technological innovation, flexibility and efficiently using resources impacts the operational success for a particular business entity. One of the most notable offerings Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides is its broad set of cloud services, in epitomized by the versatility offered with its EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) service).
Amazon Cloud even comes with a full roster of EC2 instance types, which can be overwhelming considering the choices available and the specific requirements of your workload.
Every available instance of EC2 types are optimized for different scenarios ranging from balanced compute to memory, high-performance processing, or specialized accessed storage.
Identifying the appropriate options from the listed gaps with the preset categories and their characteristics guarantees a smooth sailing for the processes optimization and results reduction for cloud infrastructure spending.
What are EC2 Instances?
At Amazon Web Services (AWS), an Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides a wide range of virtual servers termed “Instances” that differ in CPU (vCPUs), Memory, Disk Storage/Networking, and other capabilities and services.
Each configuration is sorted into families based on how the Resources are Optimized for their Workload to fit their requirements.
EC2’s Flexibility comes from its various Instance Families, allowing Businesses to quickly deploy the most suitable combination of Resource for their Websites, Databases, AI/ML Software, or Real-Time Analysis — without having to overprovision/in flat resources and trim down wasteful spending.
Detailed Overview of AWS EC2 Instance Types
1. General Purpose Instances:
General Purpose Instances allocate equal to compute, memory, networking, and other associated resources. As such, these serve a diverse array of applications that do need particular equipment.
Popular Types:
T4g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton 2 (ARM-Based)
- Description: T4g instances are burstable performance CPU instances, with baseline performance that can rise to higher levels as required. These are highly cost-effective and energy-efficient due to being powered by Graviton2.
- Use Cases: Development environments, web servers, microservices, small databases.
T3 Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable
- Description: T3 instances offer burstable CPU performance using Intel’s Turbo Boost technology. They are then deemed perfect for applications that are unsteady in terms of requiring a CPU and need periodic boosts in performance.
- Use Cases: Business applications, web applications, small-to-medium databases.
T3a Instances:
- Architecture: AMD EPYC
- Description: Offering around 10% lower cost while retaining performance features compared to T3, these powered by AMD EPYC processors are exactly like T3.
- Use Cases: Lightweight services, dev/test servers, web applications.
M7g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton3 (ARM-based)
- Description: With comparable x86 instances, the next generation General Purpose instance using Graviton3 processors delivers up to 60% better energy efficiency and 25% enhanced compute performance.
- Use Cases: Small databases, containerized applications, backend services, enterprise apps.
M6g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton2
- Description: Compared to M5, these general purpose instances outperform in price and performance by 40%. They are good for a wide range of tasks that require moderate levels of computing power, memory, and network capabilities.
- Use Cases: Caching servers, application servers, mid-size relational databases.M5 Instances
M5 Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable
- Description: Balanced General Purpose instance providing consistently great performance across a large variety of workloads. Includes improved sustain networking and high speed.
- Use Cases: Hosting web and app servers, Enterprise backend applications, Game servers.
M5a Instances:
- Architecture: AMD EPYC
- Description: Like M5 instances but with AMD EPYC. Amd powered on average will cost 10% lesser than M5 while maintaining similar performance.
- Use Cases: Business, General-purpose workloads where budget is paramount, Business applications, Caching.
2. Compute Optimized Instances
Popular Types:
C7g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton3
- Description: Reigns supreme in compute intensive workloads with clean ARM-native stacks with up to 25% improvement over compute performance on C6g.
- Use Cases: Web servers, ML inference, and video encoding. Applications: High performance web servers, ML inference, video encoding.
C6g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton2
- Description: Moderate level memory with serious amounts of compute gives you optimal output for ARM dependent workloads on AWS. Replace the C5 prized cores with C6g and you get compute optimized instances offering Graviton2 performance.
- Use Cases: Batch processing, data analytics, and high speed web applications.
C5 Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable
- Description: Gaming exactly takes the might of CPU and providing used workloads with Intel powered compute instances. You can find used-AVX 512 instruction sets enhancing performance in specific case sceneries boosting steam on segments like ad servers and scientific modeling.
- Use Cases: C5 instances are ideal for compute-intensive tasks like high-performance web servers, batch processing, HPC, and machine learning inference.
3.Memory Optimized Instances
Popular Types:
R7g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton3
- Description: The best xi for price/performance ratio on in-memory workloads, memory-optimized Graviton3 based instances.
- Use Cases: In-memory directly associated with their last scan and continue memory for caches like Redis and memory cached and set the limit with large scale databases.
R6g Instances:
- Architecture: AWS Graviton 2
- Description: Makes adaptation or RAM-bound tasks easier. This Graviton2 powered base x86 competition more cost-optimized but powered to counter best bound R5 set without fail.
- Use Cases: Powered by big data pipes to enable Einbrennen-level level numbers, super performant level 4 databases, real-time analytics, business-grade daemons.
R5 Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable
- Description: These ones are from Intel’s collection and they are built for memory bound application. They will give you great number of instance sizes and consistency on the network.
- Use Cases: SAP HANA is a popular choice among data stores in-memory for distributed analytics. These have wealth of resources insulated to GPU bound sloth processing.
R5b Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable
- Description: R5b version has an additional 60 Gbps EBS bandwidth which serves memory-intensive applications with IO needs.
- Use Cases: Scale up RDBMS, enterprise applications with great storage I/O.
4. Storage Optimized instances
Popular Types:
I4i Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon Scalable (Ice Lake)
- Description: Configuration and high performance SSD storage with NVMe SSDs designed for low latency transactional workloads.
- Use Cases: More advanced systems like NoSQL databases, real-time OLTP systems for real-time analytics.
I3 Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon E5
- Description: Older generation model of storage-optimized systems with local NVMe SSDs.
- Use Cases: Data warehousing, distributed file systems, log file processing.
I3en Instances:
- Architecture: Intel Xeon E5
- Description: Storage dense version of I3, the I3en has bigger NVMe SSD storage.
- Use Cases: File servers, largescale data processing, high throughput transactional systems.
5. Accelerated Computing Instances:
Popular Types:
P5 Instances:
- Hardware: NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs
- Description: Latest generation of GPU instances for AI/ML model training and HPC.
- Use Cases: AI/ML training, 3D rendering, high-end simulations.
INF2 Instances:
- Hardware: AWS Inferentia2
- Description: Purpose-built for high-throughput, low-latency deep learning inference at scale.
- Use Cases: AI inference workloads in production.
Trn1 Instances:
- Hardware: AWS Trainium
- Description: AI model training instances providing up to 50% better price/performance over comparable GPU-based instances.
- Use Cases: Large language models, generative AI, deep learning training.
Stats and Facts on the Types of EC2 Instances
The facts behind scaling and evolving EC2 is as follows:
- EC2 was the pioneering platform to launch in August 2006 as the first cloud-based computing platform.
- AWS offers over 500 varied types of EC2 instances globally as per the year 2025.
- T4g, M6g and C7g gained Graviton instances which added up to 40% for lower prices/performance productivity compared to x86 instances.
- With the introduction of the p5 instance family in 2023, AWS now supports up to 20 Server Petaflops of AI and HPC workload computing power.
- AWS has 32 operative regions, 102 zones, and cloud types of EC2, making them the leaders in this field.
Why CostQ.ai for AWS EC2 Optimization?
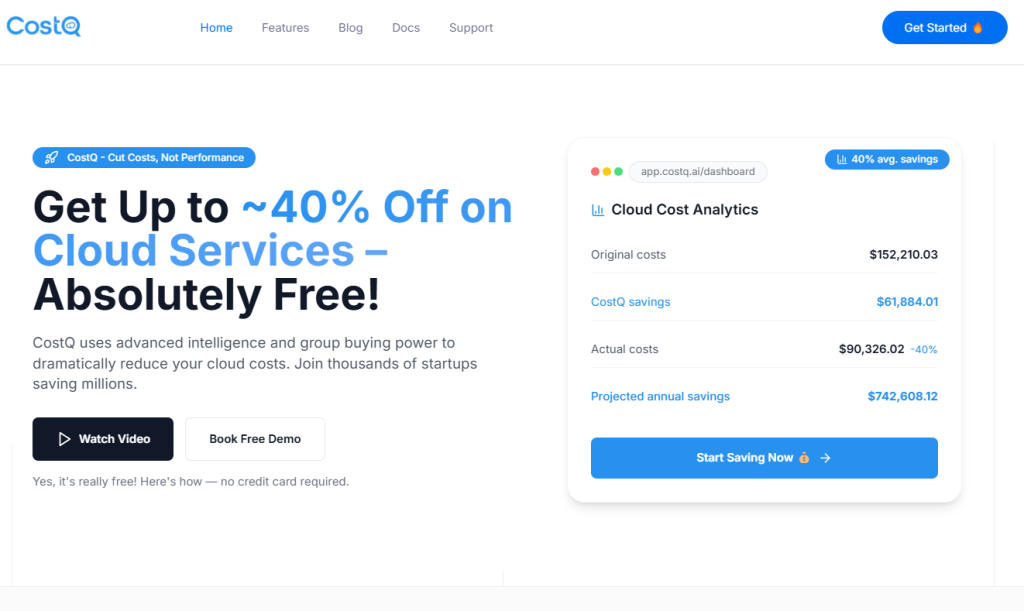
- CostQ.ai helps users manage costs on AWS EC2 with AI-enabled technology and expert optimization. Our system monitors your workloads, provides actionable recommendations, rightsizes instances and even saves you money proactively.
- CostQ.ai guarantees users proactive monitoring and automated alerts which aids in preventing unwanted expenses to the cloud. This ensures that your AWS environment is always optimized, secure and within budget.
- Using CostQ.ai enables users to save effortlessly over time, leads to smarter optimization, and allows users to scale without hesitation.
Final Words: Make the Most of Your AWS Infrastructure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Amazon EC2 instance types?
Amazon EC2 instance types refer to AWS’s set of virtual servers, each consisting of a unique “configuration” with specific features optimized for particular workloads within AWS infrastructure. EC2 instances are organized in families based on their application type which could be: general-purpose, compute optimized, memory optimized, storage optimized and accelerated computing.
2. How many EC2 instance families does AWS offer?
With more than 30 EC2 instance families available, AWS has diversified offers for clients. Each family has specific performance capabilities and has resources allocated to address varying compute, memory-intensive, and high-performance applications.
3. What are the main EC2 inst ance families?
The main families of EC2 instances are the following:
– General Purpose
– Compute Optimized
– Memory Optimized
– Storage Optimized
– Accelerated Computing
4. What is the purpose of General Purpose EC2 instances?
General Purpose EC2 instances ensure complete balance for all three resources (compute, memory and networking). This instance can handle moderate levels of computing resource without special tuning toward optimization like web server or small size databases, and development environments.
5. For what tasks can one make use of Compute Optimized EC2 instances?
The use cases for Compute Optimized EC2 instances involve applications requiring the use of high-performance processors. Compute Optimized EC2 instances are the best option for use with compute intensive tasks like for high-performance web servers, scientific modeling, batch processing and gaming servers.
6. In what way are Memory Optimized EC2 instances different from other types of EC2 instances?
Memory Optimized EC2 instances feature a high capacity of memory compared to the level of compute power given. They are ideal for memory intensive applications such as in-memory databases, big data realtime analytics, and high-performance enterprise applications.
7. What are the categories of size for the EC2 instances available?
Each EC2 instance family is offered with multiple sizes to cater to varying workloads. Standard size classifications are nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge and finally 2xlarge. The mentioned sizes balance in terms of vCPUs, memory, storage ability, and network bandwidth.
8. At the moment, how many types of EC2 are there?
The total number of versions of EC2 instances provided by AWS is over 500 from the combination of all the families, generations, and sizes of instances offered. The sited number often fluctuates because of the newer instance types added and older ones taken out by AWS.
9. What are the three most common EC2 purchase options?
When it comes to procuring EC2 instances, there are three main options to select from:
On-Demand Instances: Purchase compute capacity on a pay-per-use basis, specifically billed by the second without a long-term contract.
Reserved Instances: Make a significant cost savings when you commit to a one or three year reservation contract.
Spot Instances: Buy Amazon’s EC2 unused compute capacity and offer discount price for workloads that are flexible and fault tolerant.
10. How does one decide on the optimal type of EC2 instance to utilize?
The optimal type of EC2 instance to utilize is based on the workload requirements for the application. Requirements can be the amount of computation power, memory, storage, and network related tasks. In addition, other tools like AWS Compute Optimizer are available which make recommendations for the best instance type based on the resource usage patterns.
Related Articles You May Find Useful:
Ultimate Guide to Amazon EC2: Everything You Need to Know
Master AWS Cost Optimization in 2025 | Top Tools, Tips & Tools : Savings Tactics
How CostQ’s Compute Optimizer Cuts AWS Costs: 5 Key Areas You Can Optimize Today
